Etiology: Entamoeba muris is a one-celled organism.
Incidence: Entamoeba muris is common in gerbils.
Transmission: Transmission is fecal-oral via ingestion of infective cysts.
Distribution: Entamoeba is found in the cecum and colon.
Clinical signs: There are no clinical signs. These protozoa may proliferate in diarrheic state, however, their role as contributors to disease is poorly understood.
Diagnosis:
Antemortem: Fecal PCR can be used. Wet mount of fresh fecal material may reveal cyst forms.
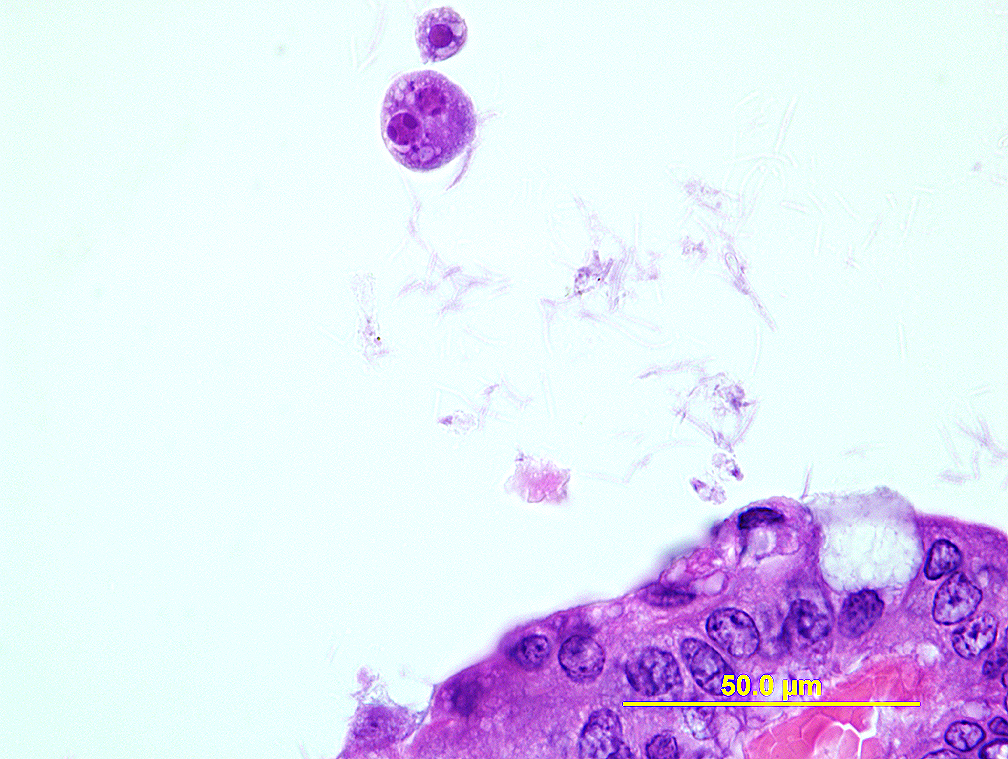
Postmortem: Wet mounts of intestinal contents may reveal cyst forms, or globular trophozoite amoebas with slow extension of pseudopods.
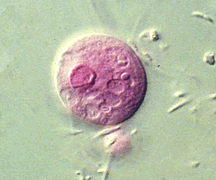
Diagnostic morphology: 15-24 µm round cyst with 1-8 nuclei (nucleus number increase from 1 to 8 with maturity) and vacuoles. Immature cysts tend to have larger and more vacuoles than mature forms. Nuclei of both amoeba and cyst form have eccentric karyosomes.