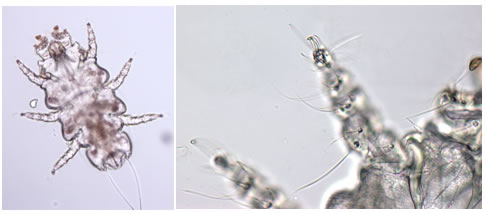
Etiology: Radfordia ensifera is the fur mite of rats.
Incidence: Incidence of infection is low.
Transmission: Fur mites are transmitted by direct contact.
Distribution: Radfordia ensifera are found in the intrascapular and dorsal cervical regions.
Clinical Signs: Clinical signs are not usually observed unless there is a heavy infestation.
Diagnosis:
Antemortem
1. PCR of skin swab or cage swab. This is the most reliable method for detection.
2. Pluck or brush hairs and examine subgrossly (use a dissecting microscope) or
microscopically for mites or eggs.
3. Run cellophane tape against the grain of the fur, place on a slide and examine
microscopically for mites or their eggs. This method is not very reliable for detection.
Postmortem
1. Place pelage (fur) samples collected in a Petri dish. As the pelage cools, mites will migrate towards the tips of the hairshafts and be visible with a dissecting microscope.
2. Place pelage samples on black construction paper. As the pelt cools, the mites will crawl away, and be visible as white specks on the black background. *Be sure to ring the edges of the construction paper with double stick tape, so that the mites do not escape the area.
Diagnostic Morphology: Paired, equal-length empodial claws on the 2nd leg.