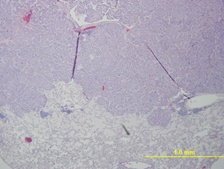
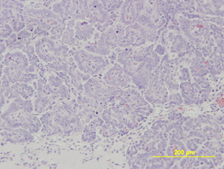
Etiology: Alveolar/bronchiolar carcinomas arise from the respiratory epithelium.
Incidence: The incidence of alveolar/bronchiolar carcinomas is low.
Clinical Signs: There are usually no clinical signs associated with this neoplasia.
Pathology: These tumors are often large and appear as white–yellow nodules which extend above the pleural surface of the lung. Histologically, the tumors are pleomorphic and may be highly infiltrative or moderately well demarcated from the surrounding lung tissue [1, 2].
Diagnosis: Diagnosis can be made upon necropsy and histopathologic examination of tissue.