Etiology: Tritrichomonas, Trichomonas species (muris, minuta, wenyoni) are one-celled, eukaryotic organisms.
Incidence: Incidence of infection is common.
Transmission: Transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route via ingestion of pseudocysts.
Distribution: These protozoa inhabit the cecal and colonic lumens. They may retrograde into the small intestine.
Clinical Signs: No clinical signs have been attributed directly to these organisms. Diarrhea may be exacerbated by the presence of these flagellates, however their role as contributors to disease is poorly defined.
Diagnosis:
Antemortem: Direct smear of feces, fecal PCR.
Postmortem: Wet mounts of cecal contents reveal slow moving, flagellated protozoa with an undulating membrane. Trichomonads move with a jerky, wobbly, undirected motion.
Diagnostic morphology: Pear- to lemon-shaped trophozoites with an undulating membrane and 3 (tri-) to 4 (tetra-) anterior flagella (A.). There is NO true cyst form.
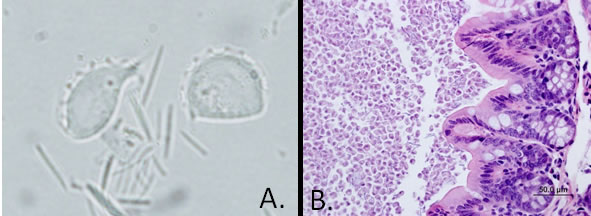
T. muris: 16-26 x 10-14 µm
T. minuta: 4-9 x 2-5 µm
T. wenyoni: 6-16 x 3-6 µm
Histopathologic examination may also be used to diagnose trichomonad infection (B.).