Etiology: Cysticercus fasciolaris (Cysticercus taeniaformis, Strobilocercus fasciolaris) are cestodes.
Incidence: Incidence of infection is uncommon in laboratory animals.
Transmission: Transmission occurs via ingestion of feed or bedding contaminated with cat fecal material. The rodent serves as the intermediate host for the cat tapeworm Taenia taeniaformis. Rodents ingest eggs in feed or bedding that has been contaminated with cat feces. Eggs develop into cysticerci (the intermediate form) in the rodent liver. The life cycle is completed when the cat (the definitive host) ingests the infected rodent.
Distribution: These cestodes are found in the rat liver.
Clinical Signs: Clinical signs are not usually observed. In heavy infections a distended abdomen may be seen.
Diagnosis:
Antemortem: Not usually possible. Cysts may be palpable if they are numerous.
Postmortem: Gross necropsy and/or histopathology.
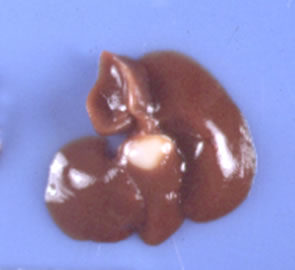
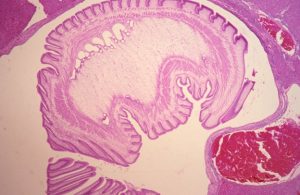
Diagnostic Morphology: 3 – 8 mm cystic (bladder like) structure filled with straw colored fluid and attached to liver. The bladder contains an inverted scolex.